Bio-based polymers, also known as biopolymers or bioplastics, are a topic of interest due to their potential to reduce the environmental impact of plastic materials. Here are some common questions that are often asked about bio-based polymers.
What are bio-based polymers?
Bio-based polymers, also known as biopolymers or bioplastics, are a class of polymers (large molecules made up of repeating subunits) that are derived from renewable biological sources. Unlike traditional plastics, which are primarily derived from fossil fuels like petroleum, bio-based polymers are produced from biomass, which can include plants, animals, or microorganisms. These materials are thought to be more environmentally friendly and sustainable because they reduce the reliance on non-renewable resources.
There are several types of bio-based polymers, and they can be categorized into two main groups:
- Biodegradable Bio-based Polymers:
- These polymers can undergo decomposition by natural processes, typically microorganisms or enzymes, into harmless substances like water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter.
- Examples of biodegradable bio-based polymers include polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), and starch-based plastics.
- Non-biodegradable Bio-based Polymers:
- These polymers are derived from renewable sources but do not readily biodegrade and can persist in the environment for an extended period.
- Examples of non-biodegradable bio-based polymers include bio-based polyethylene (bio-PE) and bio-based polypropylene (bio-PP), which are structurally similar to their fossil fuel-derived counterparts but made from bioethanol or biopropane.
Why Are Bio-based Polymers Gaining Popular Attention?
The use of bio-based polymers has gained attention in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, textiles, automotive, and consumer goods, as they are considered to offer the potential to reduce the carbon footprint and dependence on finite fossil resources. However, it’s important to note that the environmental benefits of bio-based polymers can vary depending on factors such as production methods, end-of-life disposal options, and overall sustainability practices.
Additionally, while bio-based polymers have the advantage of being derived from renewable sources, their widespread adoption faces challenges related to cost competitiveness, scalability of production, and ensuring they meet performance and regulatory requirements for specific applications. Researchers and manufacturers continue to work on improving bio-based polymer properties and developing more sustainable production processes to address these challenges.
What is a Typical Process for Creating, Producing, and Recycling Bio-Based Polymers?
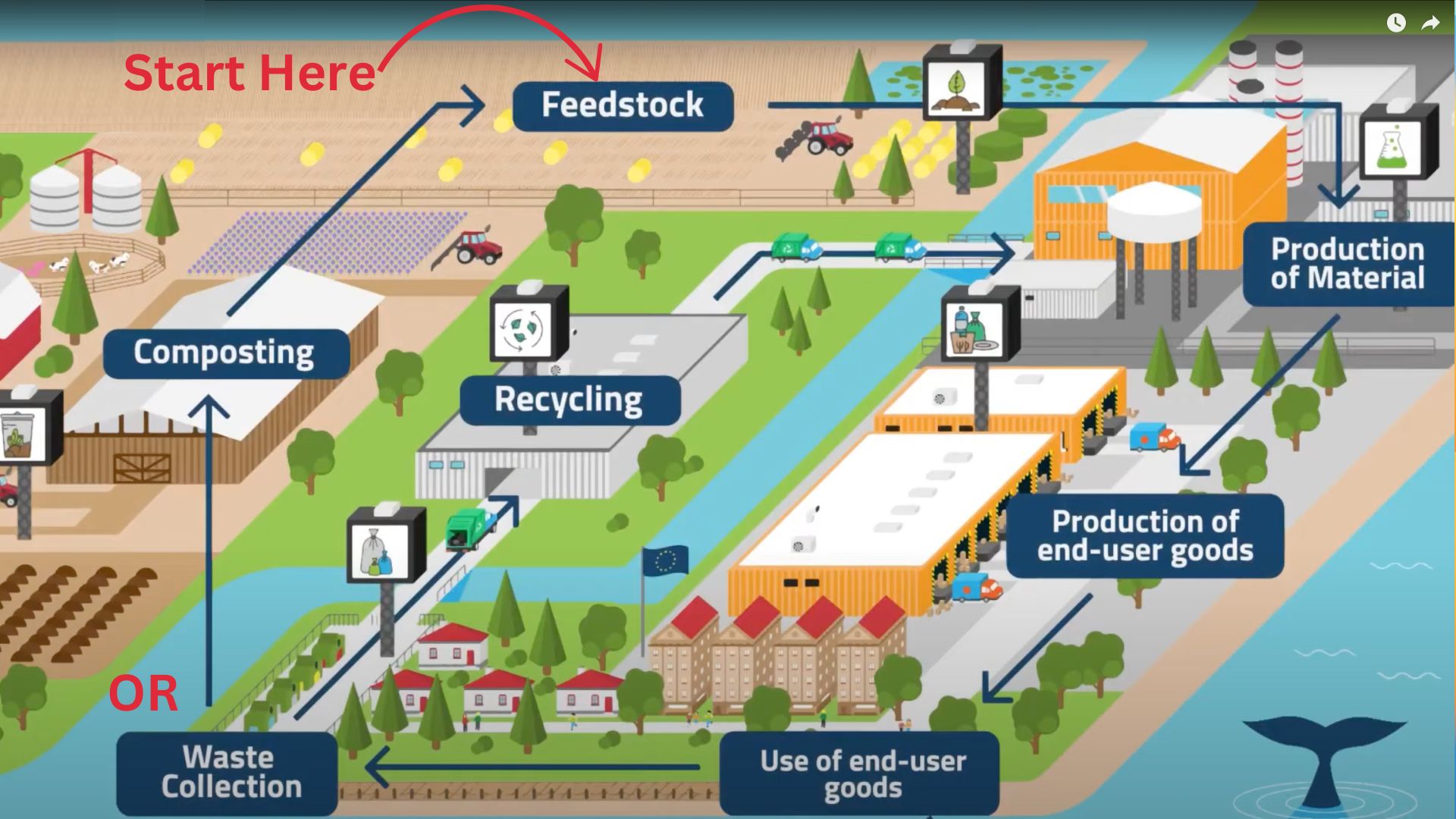
The following illustration shows the circular flow of the bio-based polymer. It begins by harvesting a bio-based source such as corn, hay, or even algae from the sea. The bio material is processed into a polymer. The bio-based polymer is produced into a consumer product. The consumer product is purchased and used. After the product has served its purpose, the waste product is recycled and returned to manufacture more bio-based polymer material. Or, the waste product is composted and used to enrich the soil to product more bio-based source material.
How are bio-based polymers different from traditional petroleum-based plastics?
Bio-based polymers and traditional petroleum-based plastics differ in several key ways, including their source materials, environmental impact, and potential applications. Here are some of the main differences:
Source Material:
- Bio-based polymers: These polymers are derived from renewable resources such as plants (e.g., corn, hay, algae, sugarcane, potatoes), animals (e.g., chitin from shrimp shells), or microorganisms (e.g., bacteria that produce polyhydroxyalkanoates or PHAs). They are made from organic compounds and are considered more sustainable because they rely on resources that can be replenished.
- Petroleum-based plastics: Traditional plastics are made from petrochemicals, which are derived from fossil fuels like crude oil and natural gas. These resources are finite, giving rise to the need to develop alternative plastics sources.



Environmental Impact:
- Bio-based polymers: Generally, bio-based polymers have a lower carbon footprint than petroleum-based plastics because they capture carbon dioxide during plant growth. However, their environmental impact can vary depending on factors like land use, farming practices, and energy consumption during production.
- Petroleum-based plastics: The production of traditional plastics is associated with environmental degradation due to resource extraction.
Biodegradability:
- Bio-based polymers: Some bio-based polymers are designed to be biodegradable, meaning they can break down naturally in the environment over time. However, it must be noted that not all bio-based polymers are biodegradable, and the rate of degradation varies widely.
- Petroleum-based plastics: Most traditional plastics are not biodegradable, nor were they designed to be, leading to contemporary issues like plastic pollution.
Applications:
- Bio-based polymers: Bio-based polymers are suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging, textiles, automotive components, and medical devices. They can replace traditional plastics in many cases, especially for single-use items.
- Petroleum-based plastics: Traditional plastics have been widely used in various industries for decades and continue to be essential for many applications due to their versatility and durability.
Recycling:
- Bio-based polymers: Recycling bio-based polymers can be more challenging than recycling traditional plastics, as they may require separate recycling streams and facilities. As noted in an article discussing biodegradable plastics made from renewable biomass, “Biodegradation is not the only acceptable end-of-life disposal pathway for biodegradable bioplastics, and mechanical and chemical recycling are often the preferred choice from the environmental point of view.”
- Petroleum-based plastics: Recycling infrastructure for petroleum-based plastics is more established, and many types of plastics can be recycled.
In summary, bio-based polymers offer the potential of a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics, but their adoption depends on factors like cost, performance, and recycling infrastructure. As you look around, you will see many common products such as plant-based food wrappers, some medical implants, biodegradable packaging like food containers and cutlery, some textiles, and even cosmetics make the list of items that incorporate bio-based polymers. As technology advances, bio-based polymers may become more competitive and widely used in various applications. Regardless of the type of plastic used, we undoubtedly depend on plastics in our daily lives.
To learn more about the wide variety of bio-based polymers available through Lone Star Chemical – PHA, PLA, PBS, PBAT, and cellulose, or to request a quote, please check out our Bio-based Polymers page.